ElasticSearch索引架构与存储
关于ES官网的介绍:
Elasticsearch provides
near real-timesearchandanalyticsfor all types of data. Whether you havestructured or unstructuredtext, numerical data, or geospatial data, Elasticsearch can efficiently store and index it in a way that supports fast searches. You can go far beyond simple data retrieval and aggregate information to discover trends and patterns in your data. And as your data and query volume grows, thedistributednature of Elasticsearch enables your deployment to grow seamlessly right along with it.
可以看到ES具有一下特点:
- 近实时
- 用于检索和分析:OLAP型数据库
- 支持非结构化数据存储:NoSQL数据库
- 分布式:支持无缝横向扩展
ES主要的使用场景如下:
- 日志、指标等数据的存储和分析;
- 复杂查询:如电商系统的商品检索、github站内检索;
- 作为冗余数据提供多样化查询方式:如SQL分库分表无法支持非分片键字段的查询,使用ES冗余数据支持多样化查询;
- 跨库关联查询:将跨库数据关联冗余至ES,关联查询直接查ES,同时解决了跨库分页的问题。
关于ElasticSearch的基本概念和原理可以参看:
官方讨论社区:discuss.elastic.co
官方博客:elastic.co/cn/blog
本文介绍了ES索引的存储架构和数据结构。
ES Index Storage Architecture
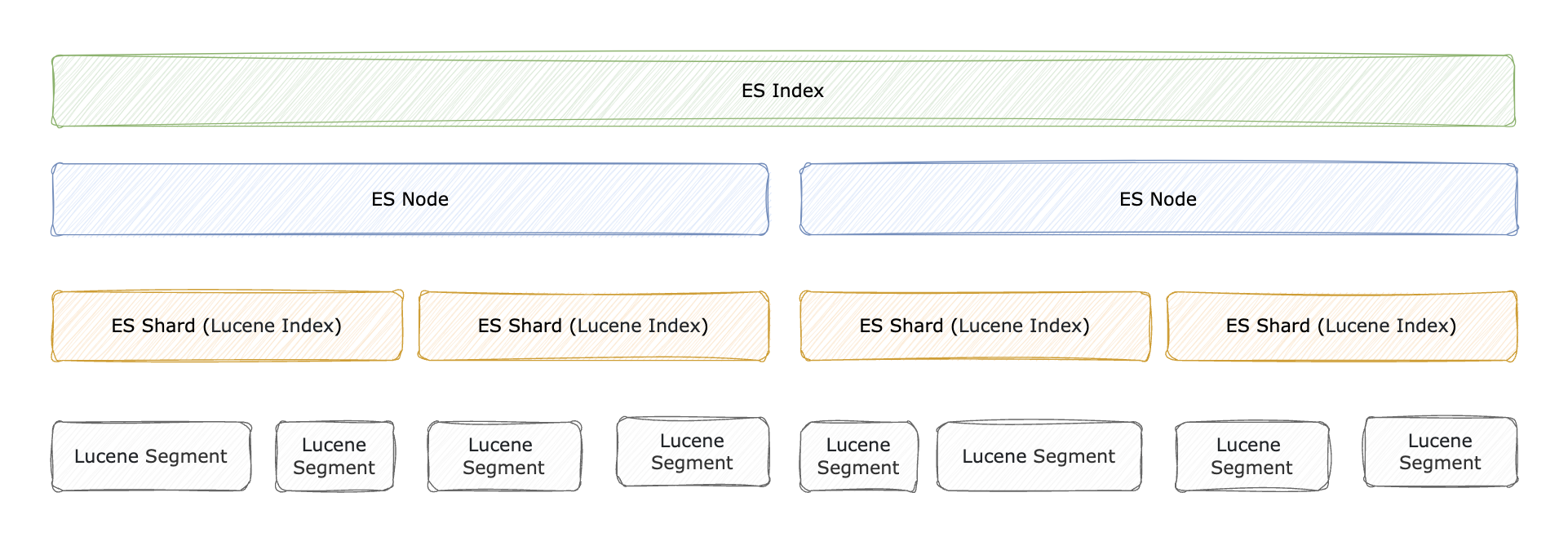
ES底层搜索使用的仍然是Lucene引擎,但Lucene只支持单节点搜索,不具备扩展性,ES在其基础上提供了分布式环境下的支持。
关于Lucene Index:
index in Lucene means “a collection of segments plus a commit point”
关于Segment:
A shard in Elasticsearch is a Lucene index, and a Lucene index is broken down into segments.
在我们变更document时,实际上会document会生成一系列数据写入Segment中,Segment中存放了Doc,Doc包含多个Field, Field包含多个Term。
写入的过程是先写入文件系统缓存(内存中)再刷到磁盘,放到文件系统缓存中即可被检索到,这个文件系统缓存刷新(refresh)间隔默认为1秒 (注意:只针对30秒内有查询的索引生效), 所以说ES准实时。同时,会有translog保证文件写入磁盘时的数据一致性,如果刷盘期间发生故障,可以通过translog进行数据恢复,等到真正把 segment 刷到磁盘(flush),且 commit 文件进行更新的时候, translog 文件才清空。
索引数据的一致性通过 translog 保证。那么 translog 文件刷盘本身如何保证一致性 ? 类比MySQL等关系数据库的处理,这里肯定有同步/异步刷盘策略, 默认情况下,Elasticsearch 每 5 秒,或每次每次 index、bulk、delete、update结束前,会强制刷新 translog 日志到磁盘上。
索引查询时会依次检索各个Segment,同时后台也会有线程执行Segment合并动作,也可以手动执行强制合并,提升Segment检索效率。 一般索引会按时间周期性新建,老的索引不再写入,这些不再写入的索引可以进行强制段合并操作,提升查询性能(一个Shard中多个Segment是串行查询的)。
- 分片内部原理
- Understanding Segments in Elasticsearch
- segment、buffer和translog对实时性的影响
- Near real-time search
- ElasticSearch中使用Index Template、Index Alias和Rollover 维护索引
- segment merge对写入性能的影响
- 段合并优化及注意事项
ES Index
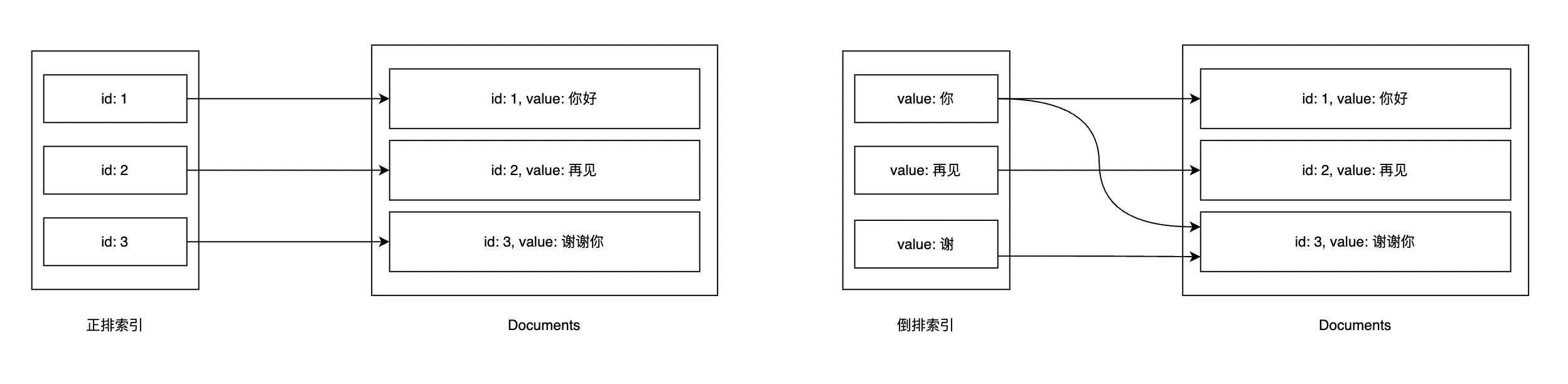
首先明确两个概念:正排索引 和 倒排索引。正派索引是根据文档(文档id)找到文档的value, 倒排索引是拿着文档的value找到对应的文档(文档id)。
ES中根据不同的字段类型和查询方式, 底层会使用不同的数据结构进行倒排索引存储,这些索引存在于内存中。
字段类型:
| 类型类别 | 类型 |
|---|---|
| Common types | binary, boolean, Keywords(keyword constant_keyword wildcard), Numbers(long double), Dates(date date_nanos), alias |
| Objects and relational types | object, flattened, nested, join |
| Structured data types | Range(long_range double_range date_range ip_range), ip, version, murmur3 |
| Aggregate data types | aggregate_metric_double, histogram |
| Text search types | text, match_only_text, annotated_text, completion, search_as_you_type, semantic_text, token_count |
| Document ranking types | dense_vector, sparse_vector, rank_feature, rank_features |
| Spatial data types | geo_point, geo_shape, point shape |
| Other types | Arrays, Multi-fields |
查询Context可分为:
- Query Context :
How well does this document match this query clause?查询结果根据 relevance score 排序; - Filter Context :
Does this document match this query clause?不参与打分,且结果会被缓存。
查询方式:
| 查询类别 | 类型 |
|---|---|
| Compound queries | bool(must, filter, should, must_not), boosting, constant_score, dis_max, function_max |
| Full text queries | intervals, match, match_bool_prefix, match_phrase, match_phrase_prefix, multi_match, combined_fields, query_string, simple_query_string |
| Geo queries | geo_bounding_box, geo_distance, geo_grid, geo_polygon, geo_shape |
| Shape queries | shape |
| Joining queries | nested, has_child has_parent |
| Match all | match_all match_none |
| Span queries | span_containing, span_field_masking, span_first, span_multi, span_near, span_not, span_or, span_term, span_within |
| Specialized queries | distance_feature, more_like_this, percolate, knn, rank_feature, script, script_score, wrapper, pinned, rule |
| Term-level queries | exists, fuzzy, ids, prefix, range, regexp, term, terms, terms_set, wildcard |
| Other | text_expansion, minimum_should_match, regexp, query_string |
Segment存储
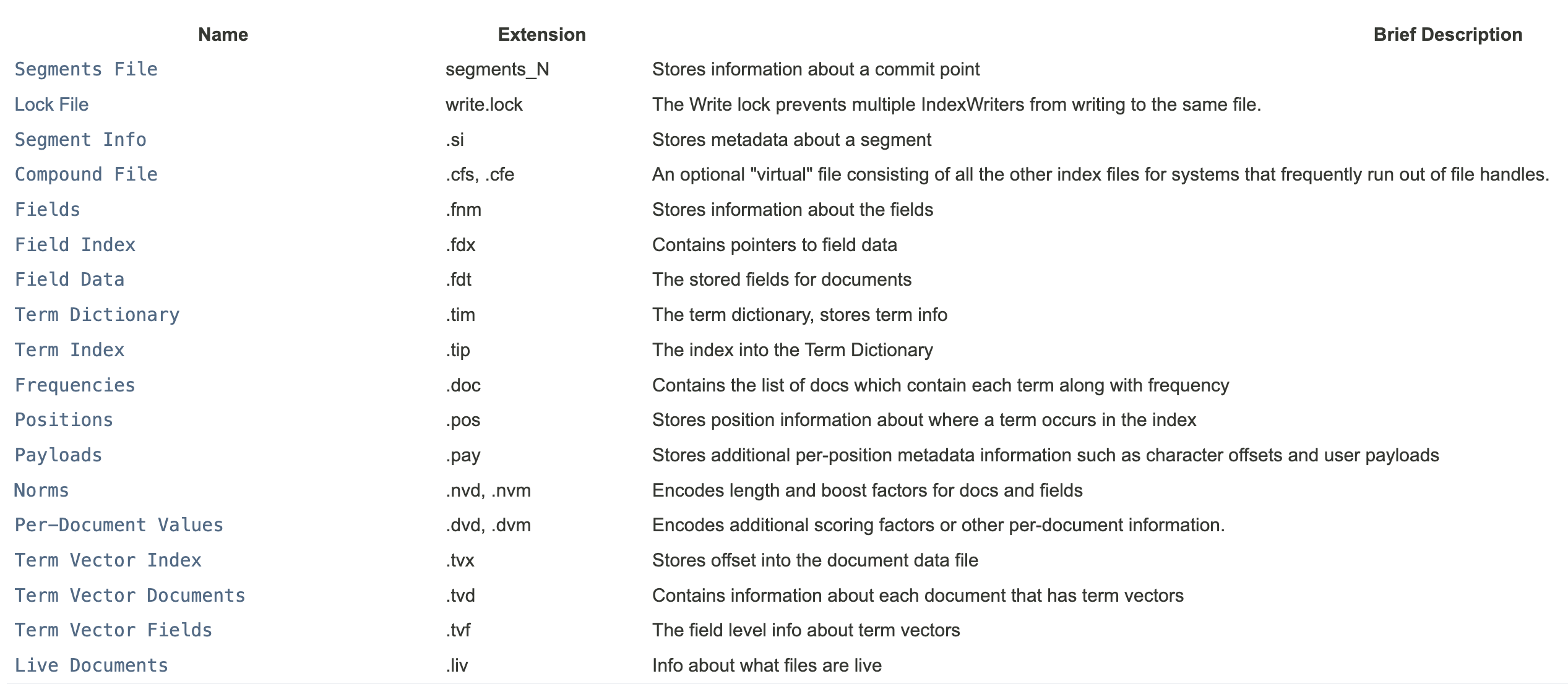
Segment中存储了以下内容(既包含正向信息,也有反向信息):
- Segment info: This contains metadata about a segment, such as the number of documents, what files it uses,
- Field names: This contains the set of field names used in the index.
- Stored Field values: This contains, for each document, a list of attribute-value pairs, where the attributes are field names. These are used to store auxiliary information about the document, such as its title, url, or an identifier to access a database. The set of stored fields are what is returned for each hit when searching. This is keyed by document number.
- Term dictionary: A dictionary containing all the terms used in all the indexed fields of all the documents. The dictionary also contains the number of documents which contain the term, and pointers to the term’s frequency and proximity data.
- Term Frequency data: For each term in the dictionary, the numbers of all the documents that contain that term, and the frequency of the term in that document, unless frequencies are omitted (IndexOptions.DOCS_ONLY)
- Term Proximity data: For each term in the dictionary, the positions that the term occurs in each document. Note that this will not exist if all fields in all documents omit position data.
- Normalization factors: For each field in each document, a value is stored that is multiplied into the score for hits on that field.
- Term Vectors: For each field in each document, the term vector (sometimes called document vector) may be stored. A term vector consists of term text and term frequency. To add Term Vectors to your index see the Field constructors
- Per-document values: Like stored values, these are also keyed by document number, but are generally intended to be loaded into main memory for fast access. Whereas stored values are generally intended for summary results from searches, per-document values are useful for things like scoring factors.
- Live documents: An optional file indicating which documents are live.
对应存储的文件如下:
可以参看:
Inverted Index
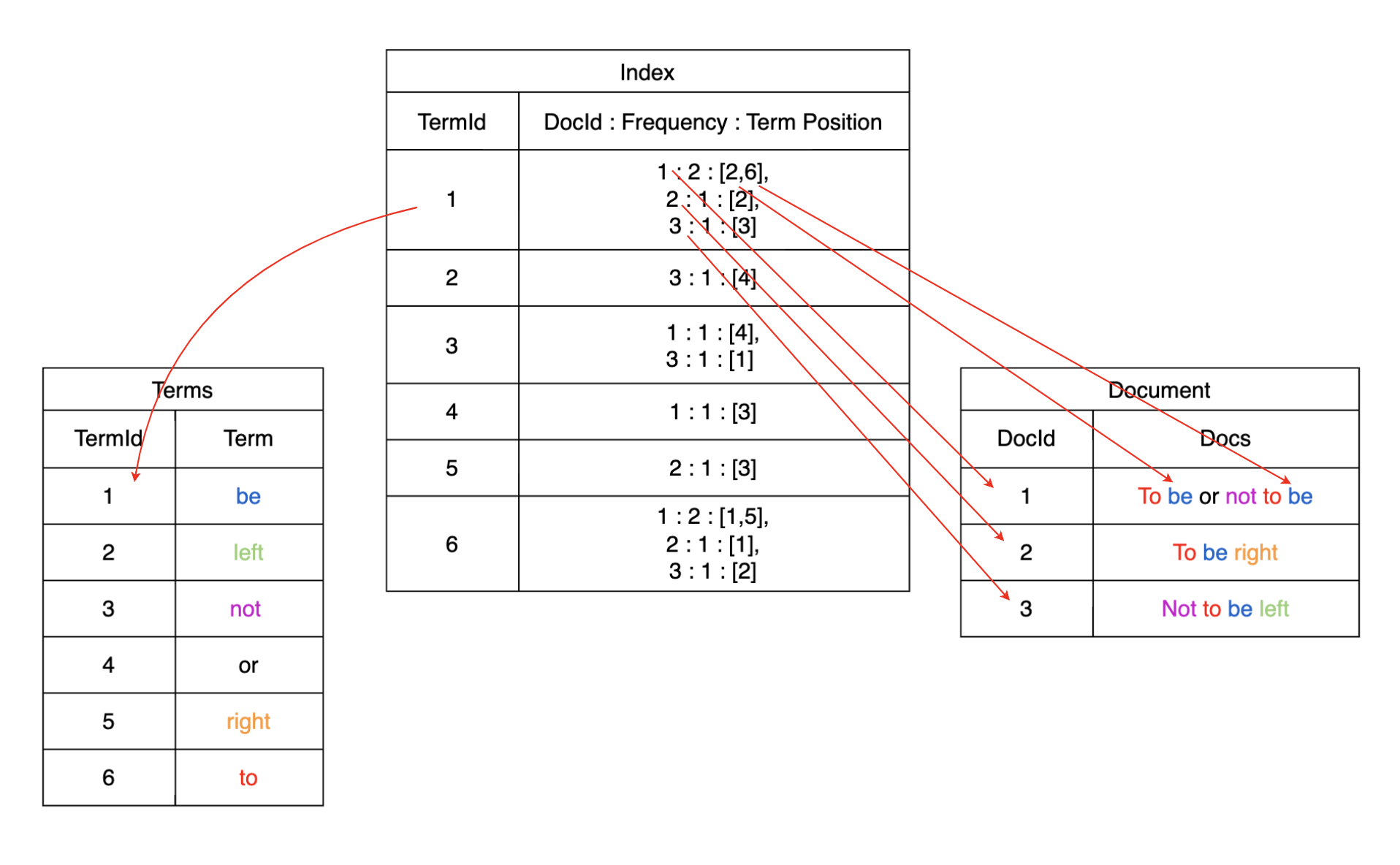
输入文本建立倒排索引的过程如下:
- 文本预处理:去除stop words,词干提取,规范化(stemming, lemmatization);
- tokenized: 将文本划分为多个terms;
- 建立term到doc的倒排索引,如下图所示。
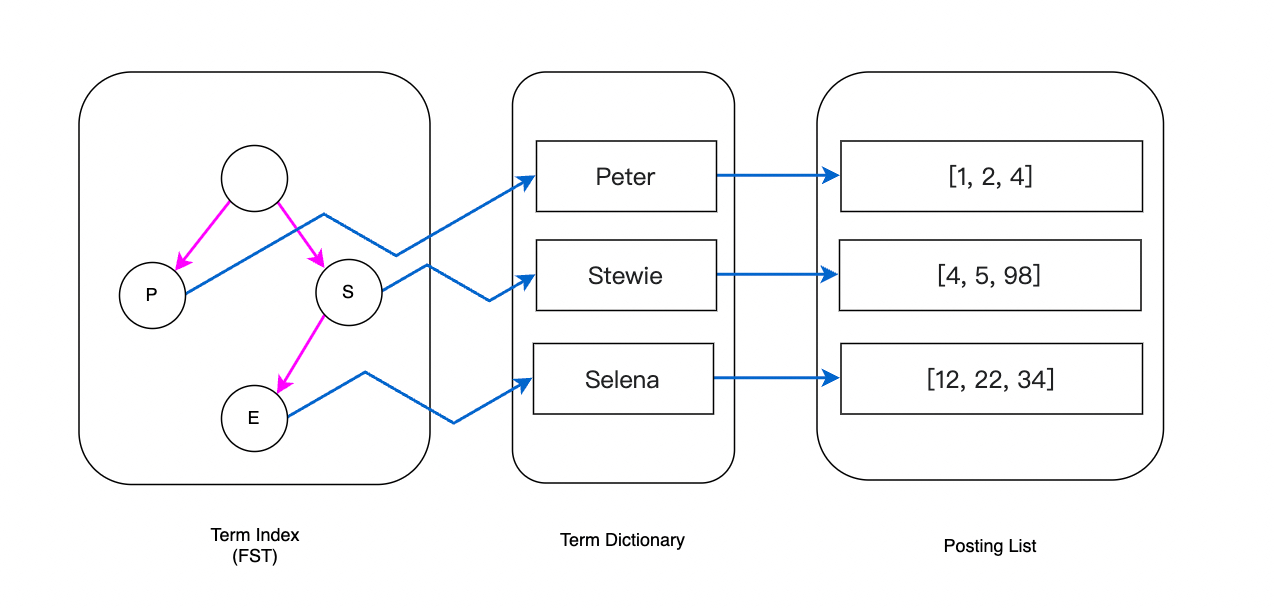
Term Index + Term Dictionary + Posting List
输入查询多个Terms,会对每个Term依次从 Term Index -> Term Dictionary -> Posting List 找到对应的DocId
Posting List
PostingList 包含文档 id、词频、位置等多个信息,这些数据之间本身是相对独立的,因此 Lucene 将 Postings List 被拆成三个文件存储:
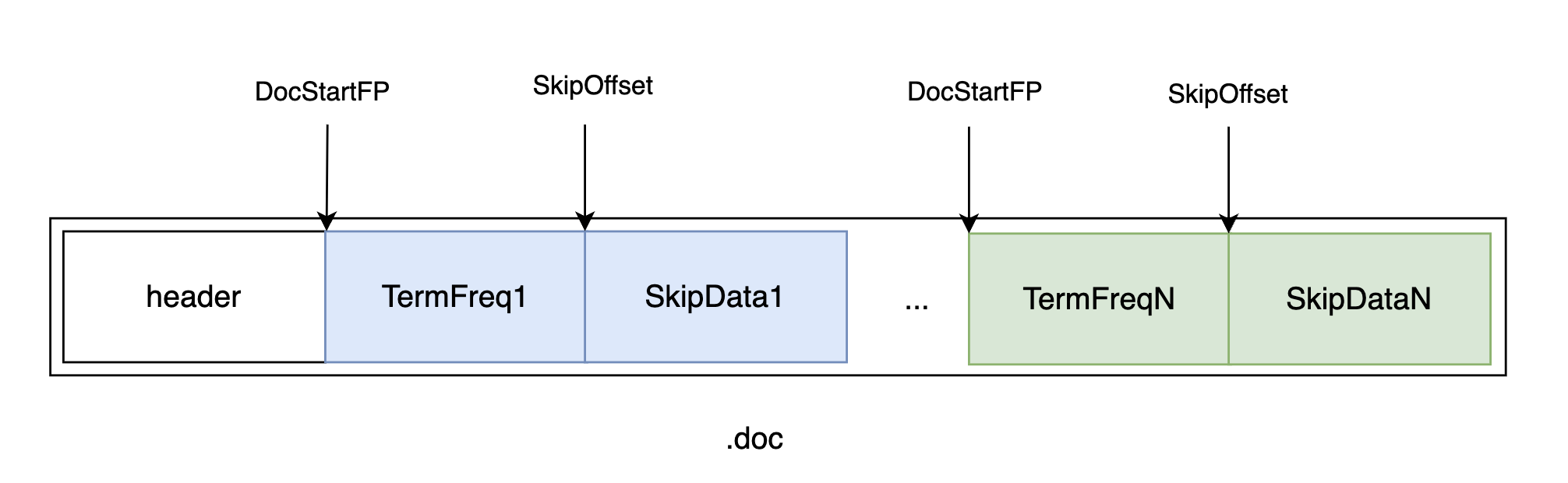
.doc后缀文件:记录 docId 信息和 Term 的词频.pay后缀文件:记录 Payload 信息和偏移量信息.pos后缀文件:记录位置信息
基本所有的查询都会用 .doc 文件获取文档 id,且一般的查询仅需要用到 .doc 文件就足够了,只有对于近似查询等位置相关的查询则需要用位置相关数据。
在 .doc 文件中,每个 Term 都包含一对 TermFreqs 和 SkipData 结构,TermFreqs中 docId 和 该Term的词频,SkipData为跳表辅助信息,用于内部跳转:
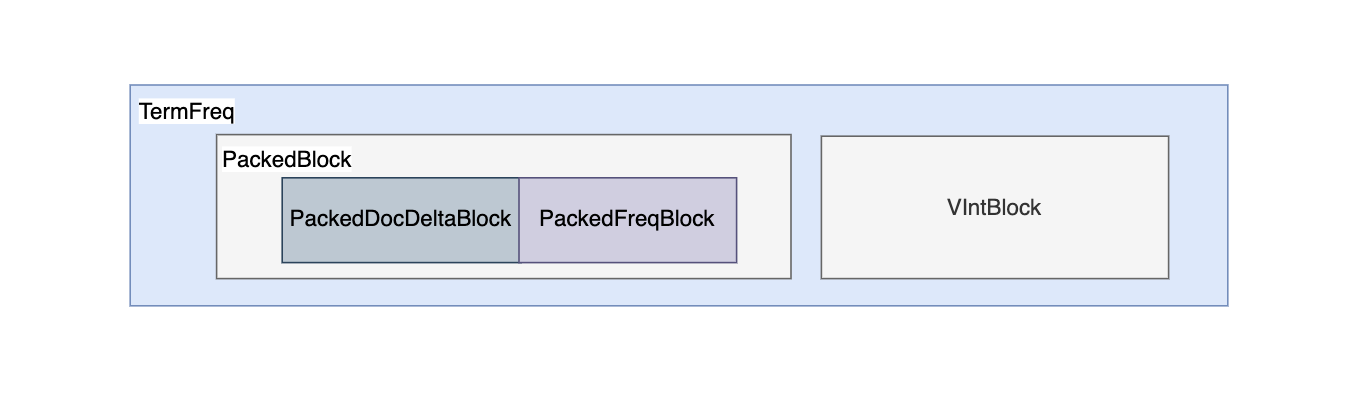
TermFreqs 存储docId及其在该doc内的词频,分别使用int值表示,但Lucene使用 PackedBlock 和 VIntBlocks 结构 压缩存储:
- PackedBlock : PackedInts 结构将一个 int[] 压缩打包成一个紧凑的 Block。它的压缩方式是取数组中最大值所占用的 bit 长度作为一个预算的长度,然后将数组每个元素按这个长度进行截取,以达到压缩的目的。
- VIntBlock : 采用 VInt 来压缩 int 值,对于绝大多数语言,int 型都占 4 个字节,不论这个数据是 1、100、1000、还是 1000,000。VInt 采用可变长的字节来表示一个整数。数值较大的数,使用较多的字节来表示,数值较少的数,使用较少的字节来表示。每个字节仅使用第 1 至第 7 位(共 7 bits)存储数据,第 8 位作为标识,表示是否需要继续读取下一个字节。
Lucene 会每处理某个 Term 的 128 个doc,其中的DocId 数组和 TermFreq 数组分别处理为 PackedDocDeltaBlock 和 PackedFreqBlock,两者构成一个PackedBlock,不足 128 的文档则采用 VIntBlock 的方式来存储。
Term Dictionary
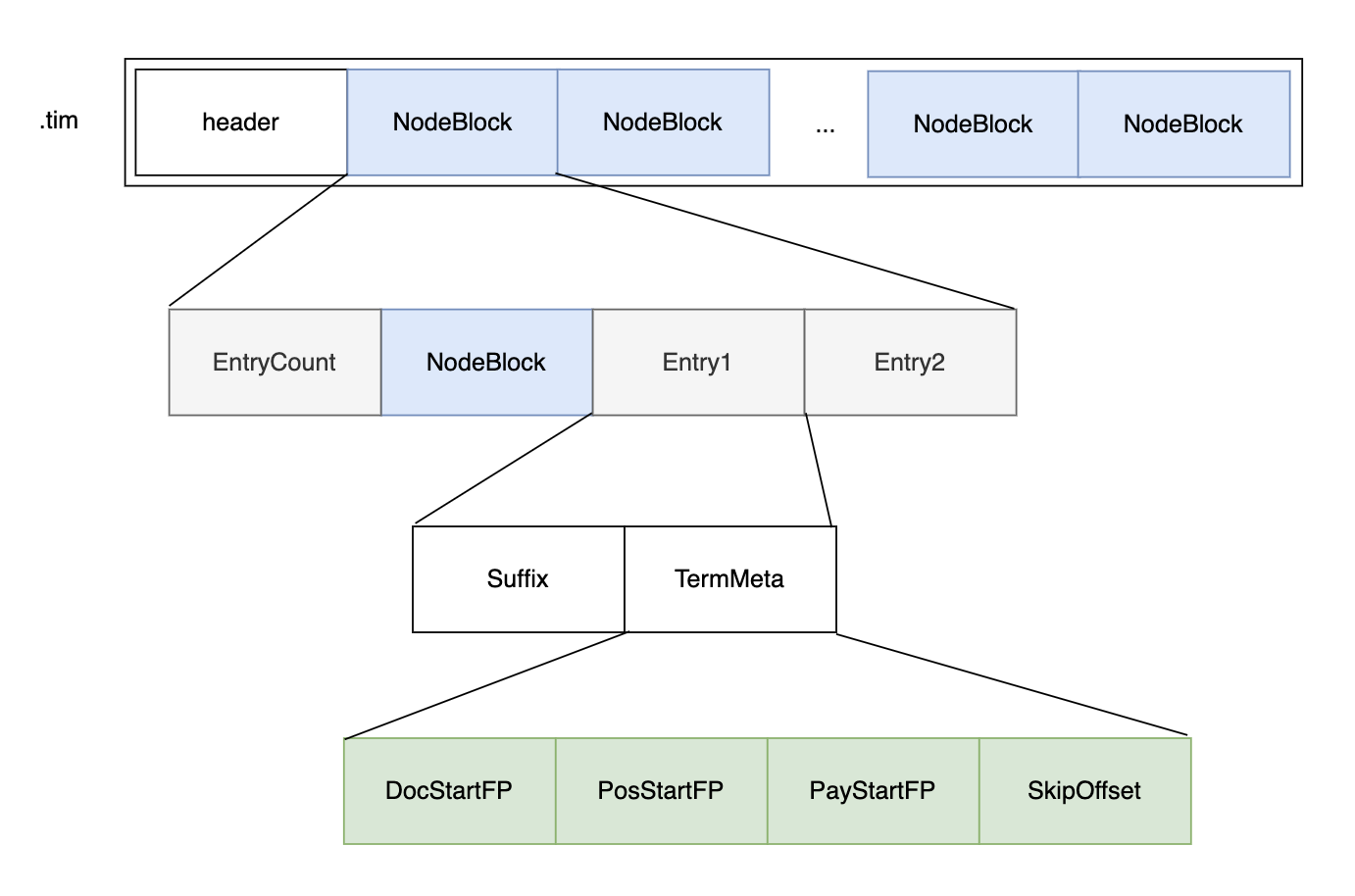
Posting List的数据如何定位呢?这就要靠Term Dictionary , Term Dictionary中存储了Term和Term在Posting List中的位置信息:
- SkipOffset: term 在 .doc 文件中跳表信息的起始位置;
- DocStartFP: term 在 .doc 文件中的 docId 与词频信息的起始位置;
- PosStartFP: term 在 .pos 文件中的起始位置;
- PayStartFP: term 在 .pay 文件中的起始位置。
Term Dictionary 存放在 .tim文件中。
内部采用 NodeBlock 对 Term 进行压缩前缀存储,处理过程会将相同前缀的的 Term 压缩为一个 NodeBlock,NodeBlock 会存储公共前缀,然后将每个 Term 的suffix 以及对应 Term 的 Posting 关联信息放入Entry。
Node Block 嵌套了 Node Block,因为Term也是嵌套的。
Term Index
当Term越来越多,从Term Dictionary中查找Term定位docId很耗时,所以进一步空间换时间,建立“索引的索引”:Term Index。
Term Index 存放在 .tip 文件中,采用有限状态转换器(Finite State Transducer, FST)数据结构组织。
FST 具有以下特点:
- 共享前缀,节省空间,适合加载到内存
- 时间复杂度O(len(inputString))
- 构建后不可变更
FST 只可以直接找到对应前缀在Term Dictionary中的NodeBlock在 .tim 文件上具体的File Pointer, 然后还需要在 NodeBlock 中遍历 Entry 匹配后缀进行查找
BKD Tree
为了优化数值类型的Range查询操作,ES采用的BKD Tree存储数值类型,其结构如下图:
但这里有一个误区,不是值是数字就应该在ES中被设置为数值类型, 例如订单号这种只有等值查询而没有数值范围查询,应设置为Keyword类型,可以参考:ES数值类型慢查询优化。