SpringBoot测试实践
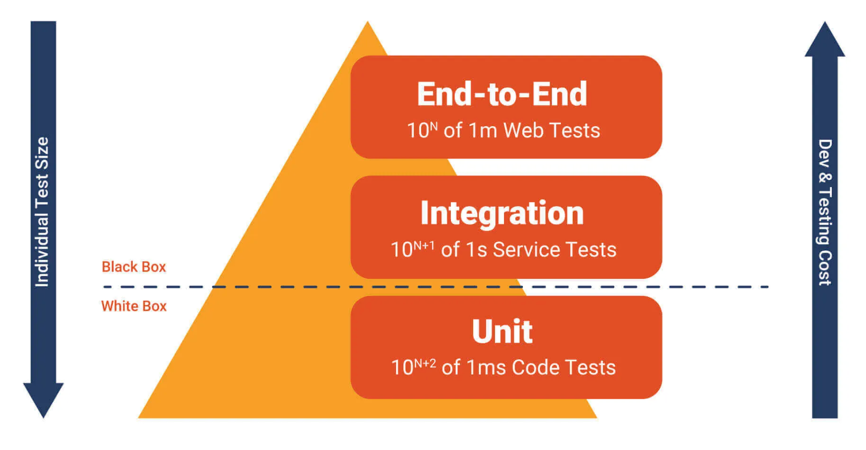
测试按照粒度可分为3层:
- 单元测试:单元测试(Unit Testing)又称为模块测试 ,是针对程序模块(软件设计的最小单位)来进行正确性检验的测试工作。程序单元是应用的最小可测试部件。在过程化编程中,一个单元就是单个程序、函数、过程等;对于面向对象编程,最小单元就是方法,包括基类(超类)、抽象类、或者派生类(子类)中的方法。
- 集成测试:整合测试(Integration Testing),又称组装测试,即对程序模块采用一次性或增值方式组装起来,对系统的接口进行正确性检验的测试工作。整合测试一般在单元测试之后、系统测试之前进行。实践表明,有时模块虽然可以单独工作,但是并不能保证组装起来也可以同时工作。该测试,可以由程序员或是软件品保工程师进行。
- 端到端测试:端到端测试(End To End Testing),又称系统测试。
通常需求开发后需要经过RD单测&自测后进行提测,提测往往需要达到一定的单测/自测代码覆盖率,或者某些基本case通过(冒烟测试),符合提测要求后QA对整体功能进行端到端测试。
完善的测试流程有助于提升代码质量和研发效率,这中间一方面对RD自身的业务素养有要求,另一方面对团队研发流程的规范性有要求。
成熟的研发流程和体系应减少“人性”带来的不稳定性,测试即是应对该不稳定性的有效方法之一。
本文记录了结合SpringBoot进行测试的一些案例,示例代码参见: spring-boot-test-sample
注意区分JUnit4和JUnit5的注解,本文代码基于JUnit4
首先我们引入依赖:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
<dependencies>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.projectlombok/lombok -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mockito</groupId>
<artifactId>mockito-core</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mockito</groupId>
<artifactId>mockito-junit-jupiter</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.powermock</groupId>
<artifactId>powermock-module-junit4</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.powermock</groupId>
<artifactId>powermock-api-mockito2</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.6.13</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mockito</groupId>
<artifactId>mockito-core</artifactId>
<version>2.28.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mockito</groupId>
<artifactId>mockito-junit-jupiter</artifactId>
<version>2.28.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.powermock</groupId>
<artifactId>powermock-module-junit4</artifactId>
<version>2.0.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.powermock</groupId>
<artifactId>powermock-api-mockito2</artifactId>
<version>2.0.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
Mockito & PowerMockito 单元测试
当我们仅仅需要验证代码逻辑,不需要Spring的bean注入时,使用Mockito & PowerMockito来快速测试。
Mockito用于mock对象便于对代码逻辑进行测试&验证,但Mockito mock的方法有限,无法mock final、private、static方法,而PowerMockito框架弥补了这一点。两者可以混合使用。
案例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
@RunWith(PowerMockRunner.class)
// mock static method
@PrepareOnlyThisForTest({SampleUtil.class})
@PowerMockIgnore({"javax.net.ssl.*","javax.management.*", "javax.security.*", "javax.crypto.*"})
// 如果SampleUtil中有静态字段,这里抑制静态字段初始化,否则会报错
@SuppressStaticInitializationFor("com.a.b.c.SampleUtil")
public class UnitTest {
@Mock
private SampleRepository sampleRepository;
@InjectMocks
private SampleService sampleService;
@BeforeClass
public static void beforeAll(){
System.out.print("\n\n\n++++++++++++++\n\n\n");
}
@AfterClass
public static void afterAll(){
System.out.print("\n\n\n==============\n\n\n");
}
@Before
public void before(){}
@After
public void after(){}
@Test
public void getSamples() throws JSONException {
PowerMockito.mockStatic(SampleUtil.class);
// 注意所有when内部的方法参数必须用org.mockito.ArgumentMatchers的方法包一层,不能直接传
PowerMockito
.when(SampleUtil.getSomething(eq("1"))) // 反例:.when(SampleUtil.getSomething("1"))
.thenReturn(1L);
PowerMockito.when(sampleRepository.selectSamples(argThat(id -> id.equals(1L))))
.thenReturn(new ArrayList<>());
PowerMockito.when(sampleRepository.selectSamples(argThat(new GreaterOrEqual<>(1L))))
.thenReturn(new ArrayList<>());
// 这里有any(),anyString()等
// 如果参数是String,mock方法传入的是null,则mock不生效,传null需指定为any()
Mockito
.when(sampleRepository.selectSamples(any()))
.thenReturn(new ArrayList<>());
// verify方法调用次数
Mockito.verify(sampleRepository, Mockito.times(1)).selectSamples(any());
// Mockito.verify(sampleRepository, Mockito.times(1)).selectSamples(argThat(i->i.equals(1)));
// capture参数验证
ArgumentCaptor<Long> paramCap = ArgumentCaptor.forClass(Long.class);
Mockito.verify(sampleRepository, Mockito.times(1)).selectSamples(paramCap.capture());
Assert.assertNotNull(paramCap.getValue());
// 运行参数中的Runnable
Mockito.doAnswer(invocation -> {
Object[] arguments = invocation.getArguments();
Runnable runnable = (Runnable)arguments[0];
runnable.run();
return null;
}).when(sampleRepository).run(any(Runnable.class));
List<Sample> samples = sampleService.listSamples("1");
// 如果sample.size()返回Long,需要加一个 sample.size().longValue()方法
Assert.assertEquals(0,samples.size());
// 比较JSON
JSONAssert.assertEquals("{\"a\":1}","{\"a\":1}",false);
// 解析JSON
Assert.assertEquals(JsonPath.parse("{\"a\":1}").read("$.a").getClass(),Integer.class);
}
@Test
public void mockPrivate() {
try {
Method method = PowerMockito.method(Sample.class, "privateMethodName", Long.class);
method.invoke(sampleService, 0L);
Assert.fail();
} catch (Exception e) {
Assert.assertEquals("报错信息", e.getCause().getMessage());
}
}
}
@Mock和@MockBean使用格式:Mockito.when(localVar.method()).thenXxx…
@Spy和@SpyBean使用格式:Mockito.doXxx().when(localVar).method()
使用不当会报NPE
Spring 测试
当依赖Spring时,可以利用Spring和PowerMockito一起完成mock和test
案例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
@RunWith(PowerMockRunner.class)
@PowerMockRunnerDelegate(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@PrepareOnlyThisForTest({SampleUtil.class})
@ContextConfiguration(classes = ControllerSliceTestWithPowerMockito.Context.class)
public class ControllerSliceTestWithPowerMockito {
// @Import加入需要扫描的Bean
// @Configuration配合其他都行,参考@ContextConfiguration注释
@Import(SampleController.class)
static class Context {
}
@MockBean
private SampleService sampleService;
@SpyBean
private SampleConverter sampleConverter;
@Test
public void zkSetup() {
PowerMockito.mockStatic(SampleUtil.class);
PowerMockito.when(SampleUtil.getSomething(eq("a")))
.thenReturn(1L);
sampleConverter.test();
// assert, verify
}
}
WebMvc 切片测试
- @AutoConfigureWebMvc : Use this if you need to configure the web layer for testing but don’t need to use MockMvc
- @AutoConfigureMockMvc : Use this when you just want to configure MockMvc
- @WebMvcTest : Includes both the @AutoConfigureWebMvc and the @AutoConfigureMockMvc, among other functionality.
三者区别,参考:What’s the difference between @AutoConfigureWebMvc and @AutoConfigureMockMvc?
案例一:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
@WebMvcTest(SampleController.class)
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = TestSampleController.TestContext.class)
public class TestSampleController {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(TestSampleController.class);
// 这里填入需要扫描的Bean,这样就不用扫描整个project文件,加快测试速度
@Import({SampleController.class, ControllerExceptionAdvice.class})
@Configuration // 这里兼容老版本,高版本不用加
static class TestContext {
}
@Autowired
private MockMvc mockMvc;
@MockBean
private SampleService sampleService;
// 这里用SpyBean注解:当SampleController中用到了SampleConverter,但是又不需要mock,得用converter原本的逻辑
// 或用@MockBean时,在 Mockito.when(...).thenCallRealMethod()就行。
@SpyBean
private SampleConverter sampleConverter;
@Before
public void prepareMock() {
// 对SampleController中调用了的SampleService的方法进行mock
Mockito
.doNothing()
.when(sampleService)
.sampleMethod(Mockito.any());
}
@Test
public void shouldReturnSuccess() throws Exception {
SampleRequest req = new SampleRequest();
req.setA(1L);
String bodyJson = JsonUtils.toJson(req);
mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders
.post("/test")
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.content(bodyJson))
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk())
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.content().contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8))
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.content().json("{\"success\":true}"));
}
@Test
public void shouldReturnErrorMsg() throws Exception {
SampleRequest req = new SampleRequest();
req.setB
String bodyJson = JsonUtils.toJson(req);
mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders
.post("/test2")
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.content(bodyJson))
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk())
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.content().contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8))
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.content().json("{\"success\":false,\"errorMsg\":\"错误信息\"}"));
}
}
案例二:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
@RunWith(PowerMockRunner.class)
@SuppressStaticInitializationFor("com.dianping.cat.Cat")
// mock static method
@PrepareForTest({SampleUtil.class})
// spring bean
@PowerMockRunnerDelegate(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@PowerMockIgnore({"javax.net.ssl.*","javax.management.*", "javax.security.*", "javax.crypto.*"})
// @SpringBootTest从当前包向上找@SpringBootConfiguration,或者指定
@SpringBootTest(classes = SpringTestCommonConfig.class)
public class SpringBeanTest {
// 这个mock对象会注入Spring容器
@MockBean
private SampleRepository sampleRepository1;
// 真实调用该对象逻辑
@SpyBean
private SampleRepository sampleRepository2;
@Autowired
private SampleRepository sampleRepository3;
@Autowired
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Autowired
private SampleConfig sampleConfig;
@Test
public void sampleBeanTest() throws JSONException {
SampleRepository bean = applicationContext.getBean(SampleRepository.class);
Assert.assertEquals(sampleRepository1,bean);
}
}
此外我们使用h2内存数据库达到对Mapper的测试,也有testcontainers库推出用于测试与外部系统的交互,这里不赘述,详见示例代码