SpringBoot application.yml/.properties配置文件加载过程
参考:Springboot源码之application.yaml读取过程
当SpringBoot版本<2.4.0时:
SpringBoot配置文件一般为application.yml或application.properties等,其加载流程在SpringApplication的run()方法中的ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);中完成,当环境准备好会触发EventPublishingRunListener implement SpringApplicationRunListener的 environmentPrepared()方法,该方法广播ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent,该事件有一个ConfigFileApplicationListener implements EnvironmentPostProcessor, SmartApplicationListener, Ordered监听器,该类用于加载配置文件。以上具体的调用过程如下: 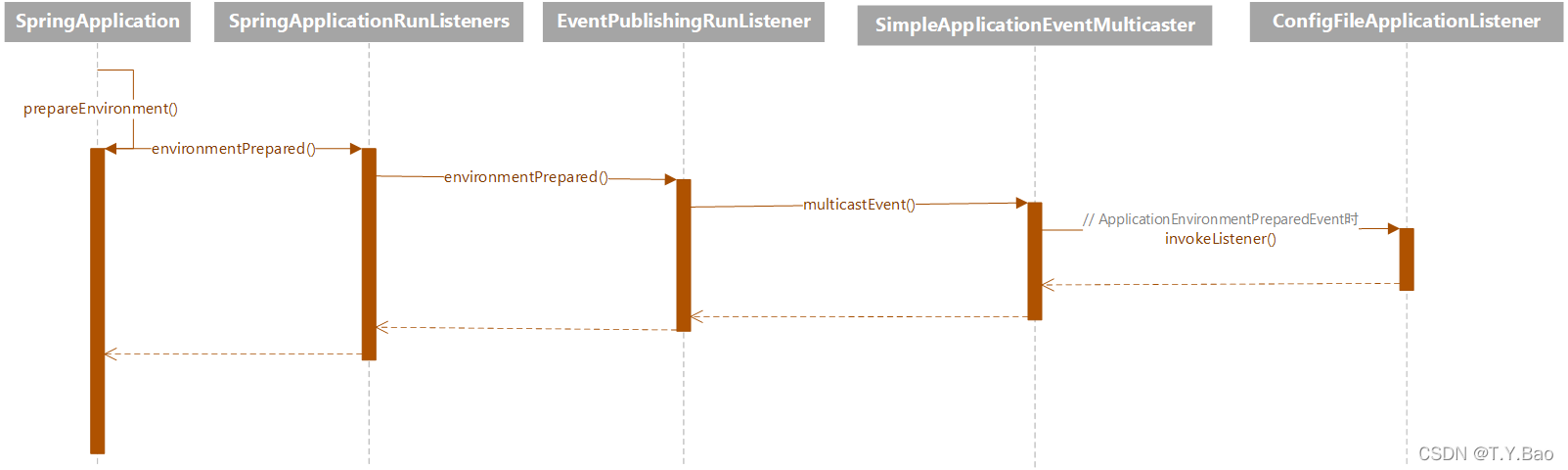 具体看看
具体看看ConfigFileApplicationListener这个类如何加载配置文件的:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
public class ConfigFileApplicationListener implements EnvironmentPostProcessor, SmartApplicationListener, Ordered {
...
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
// 向下转型
if (event instanceof ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent((ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) event);
}
if (event instanceof ApplicationPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationPreparedEvent(event);
}
}
private void onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event) {
// 获取所有的EnvironmentPostProcessor对象
List<EnvironmentPostProcessor> postProcessors = loadPostProcessors();
// this对象也是一个EnvironmentPostProcessor,加入
postProcessors.add(this);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(postProcessors);
for (EnvironmentPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
// 遍历进行环境后置处理
// 当处理到this时,加载文件,会调用this.postProcessEnvironment
postProcessor.postProcessEnvironment(event.getEnvironment(), event.getSpringApplication());
}
}
...
@Override
public void postProcessEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplication application) {
addPropertySources(environment, application.getResourceLoader());
}
protected void addPropertySources(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
RandomValuePropertySource.addToEnvironment(environment);
// 正式开始load
new Loader(environment, resourceLoader).load();
}
}
// 这里用来循环location,点开getSearchLocations()可以看到配置文件的路径搜索顺序(LinkedHashSet是有序的)如下:
// "file:./config/"
// "file:./config/*/"
// "file:./"
// "classpath:/config/"
// "classpath:/"
private void load(Profile profile, DocumentFilterFactory filterFactory, DocumentConsumer consumer) {
getSearchLocations().forEach((location) -> {
boolean isDirectory = location.endsWith("/");
// 用来循环配置文件名称,一般只有一个就是application,除非设置spring.profiles.active项
Set<String> names = isDirectory ? getSearchNames() : NO_SEARCH_NAMES;
names.forEach((name) -> load(location, name, profile, filterFactory, consumer));
});
}
private void load(String location, String name, Profile profile, DocumentFilterFactory filterFactory,
DocumentConsumer consumer) {
if (!StringUtils.hasText(name)) {
for (PropertySourceLoader loader : this.propertySourceLoaders) {
if (canLoadFileExtension(loader, location)) {
load(loader, location, profile, filterFactory.getDocumentFilter(profile), consumer);
return;
}
}
throw new IllegalStateException("File extension of config file location '" + location
+ "' is not known to any PropertySourceLoader. If the location is meant to reference "
+ "a directory, it must end in '/'");
}
Set<String> processed = new HashSet<>();
// PropertySourceLoader有两个实现类:PropertiesPropertySourceLoader和YamlPropertySourceLoader
// 前者用于搜索properties和xml文件
// 后者用于搜索yml和yaml文件
for (PropertySourceLoader loader : this.propertySourceLoaders) {
// 遍历后缀文件名,
for (String fileExtension : loader.getFileExtensions()) {
if (processed.add(fileExtension)) {
// 这里load
loadForFileExtension(loader, location + name, "." + fileExtension, profile, filterFactory,
consumer);
}
}
}
}
当SpringBoot版本>=2.4.0时:
上文中ConfigFileApplicationListener类于2.4.0版本被废弃,取而代之的是ConfigDataEnvironmentPostProcessor,所有的EnvironmentPostProcessor通过EnvironmentPostProcessorApplicationListener调用,该ApplicationListener的顺序Order为Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10(而bootstrap.yaml等文件的BootstrapApplicationListener的顺序Order为Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 5,所以boostrap先于application解析,同样application会覆盖boostrap配置),整个调用链路如下:
SpringApplication#run -> SpringApplication#prepareEnvironment->SpringApplicationRunListeners#environmentPrepared -> 系列ApplicationListener按照Order从小到达执行 通过这两个类的注释也可以看出:
之前加载application.yml or properties文件和springboot是耦合在一个ConfigFileApplicationListener中,也就是说,只有调用springboot的这个监听器才能解析配置文件,而现在SpringBoot这里==抽象==出了加载文件的过程。
先来看一下org.springframework.boot:spring-boot.jar包下的$META-INF$的spring.factories文件,需要注意以下三个key:value: 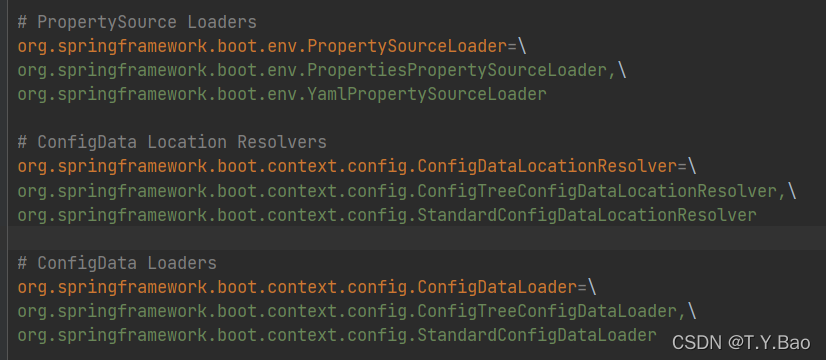
看到下面两个接口属于同一个包,显然是有一定联系的。看看它们的注释:
ConfigDataLocationResolver: Strategy interface used to resolve {@link
ConfigDataLocationlocations} into one or more {@linkConfigDataResourceresources}. ConfigDataLoader: Strategy class that can be used to load {@linkConfigData} for a given{@link ConfigDataResource}.
再看第一个接口:
PropertySourceLoader: to load a {@link
PropertySource}.
实际上,在加载springboot配置文件的过程中StandardConfigDataSource extends ConfigDataSource中通过字段StandardConfigDataReference reference 的字段方法PropertySourceLoader.load()来实现ConfigDataLoader.load()。这个StandardConfigDataReference既有 ConfigDataLocation 也有PropertySourceLoader,起到了承上启下的reference作用。结构图如下: 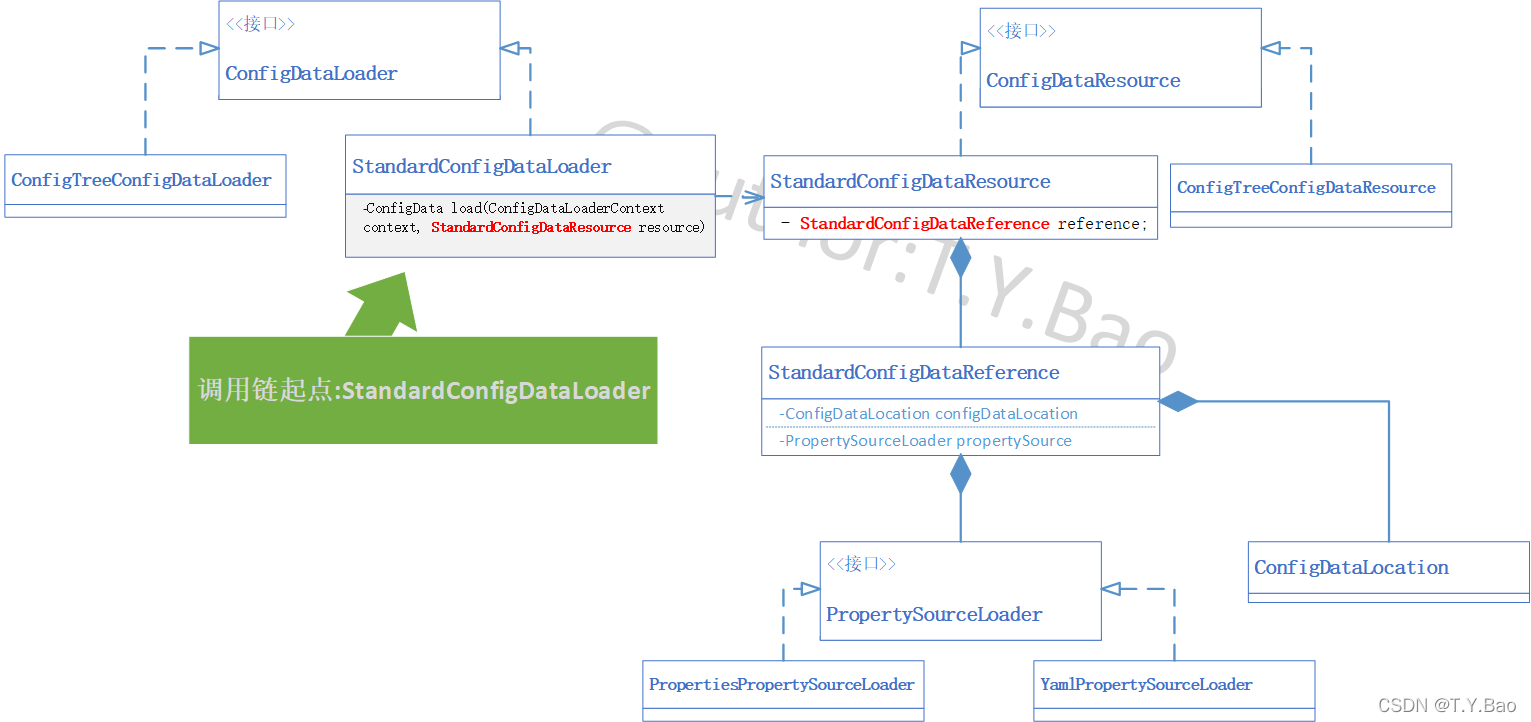
至于StandardConfigDataLoader怎么调用的,我就不画图了,流程如下: ConfigDataEnvironmentPostProcessor的postProcessEnvironment()$\rightarrow$ConfigDataEnvironment的processAndApply()$\rightarrow$同类中的processInitial()$\rightarrow$ConfigDataEnvironmentContributors的withProcessedImports()$\rightarrow$ConfigDataImporter的resolveAndLoad()$\rightarrow$同类的load()$\rightarrow$ConfigDataLoaders的load()$\rightarrow$StandardConfigDataLoader的load()。